Bioreactor
A woodchip bioreactor removes nitrates from tile drainage. The woodchips act as a carbon source for denitrifying bacteria, and as they become saturated, low oxygen conditions promote denitrification.
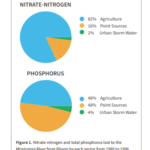
Illinois Nutrient Loss Reduction Strategy & Agricultural Conservation Practices
This 1-pager created by Illinois Extension, gives a brief overview of the Illinois Nutrient Loss Reduction Strategy (INLRS), highlights nutrient loss in Illinois, impacts of nutrient loss, and conservation practices that can address in-field and edge of field nutrient loss.
Download Documents
ISAP’s Edge-of-Field Incentive Directory
ISAP’s Edge-of-Field Incentives Directory provides an overview of edge-of-field (EoF) incentive payment opportunities for farmers in Illinois. EoF practices are defined as those practices which intercept, capture, and treat subsurface drainage (conservation drainage practices) or surface runoff at the field level. The conservation drainage practices include bioreactors, constructed wetlands for tile-drainage treatment, drainage water management, drainage water recycling, and saturated buffers. Surface runoff practices include vegetated riparian buffers, filter strips, prairie strips, and restored wetlands. The directory also includes a “Stacking Matrix” so farmers can easily determine if they may be eligible to stack payments from multiple programs.
Download Documents
Michigan State University Drainage Resources
This Michigan State University Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering website provides education and practical solutions to address drainage issues.
View Website
University of Illinois Woodchip Bioreactor
Simple woodchip-filled trenches called bioreactors can clean nitrogen pollution from water. Find out more from Dr. Laura Christianson of the University of Illinois as she talks about one of her favorite ideas.
Watch Video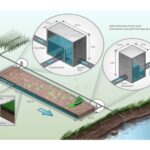
ADMC Bioreactor
This ADMC webpage provides information on bioreactors including considerations for installation and financial impacts.
View Website
NRCS Bioreactor Conservation Practice Standard Factsheet
This one page factsheet from NRCS provides an overview of woodchip bioreactors, how they fuction, and the benefits they provide.
View Website